AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity: WHO
List of 10 threats to global health in 2019:
- Air pollution and climate change
- Noncommunicable diseases
- Threat of a global influenza pandemic
- Fragile and vulnerable settings, such as regions affected by drought and conflict
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Ebola and high-threat pathogens
- Weak primary care
- Vaccine hesitancy
- Dengue
- HIV
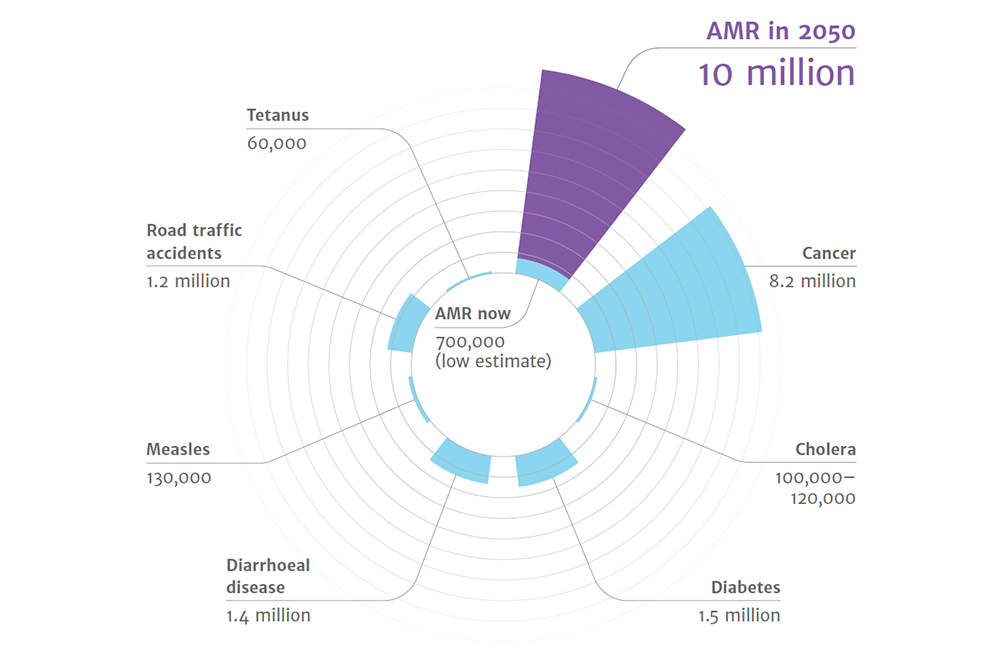
10 million people are projected to die from resistant infections by 2050, AMR alone will be killing more people than cancer and road traffic accidents combined together: The Lancet
- The cost of AMR to the economy is significant. In addition to death and disability, prolonged illness results in longer hospital stays, the need for more expensive medicines and financial challenges for those impacted.
- Misuse and overuse of antimicrobials are the main drivers in the development of drug-resistant pathogens.
100 Million Indians could be carrying NDM-1 Gene (one of the most difficult to treat form of antibiotic resistant gene): JAC
Drug-resistant infections can strike anyone—young or old, healthy or sick. Treating resistant infections costs the U.S. health care system an estimated $21 billion to $34 billion annually according to IDSA, we can only imagine the corresponding situation in a developing country like India.
Antibiotic resistance also complicates a variety of important medical procedures, including cancer chemotherapy, solid organ and bone marrow transplants, joint replacements, and other complex surgeries. The safety of these procedures depends upon the availability of effective antibiotics.